
In the first part I am explaining how to do export and import using js.
here is my sample module ‘myutile.js‘
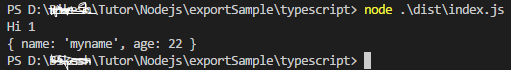
const myMethod1 = () => { console.log('Hi 1') } const myMethod2 = () => { console.log('Hi 2') } const myData = { name:'myname', age:22 } module.exports = { myMethod1, myMethod2, myData };
we can import all from the above module
var access1 = require('./myutile'); access1.myMethod1(); access1.myMethod2(); console.log(access1.myData);
output:
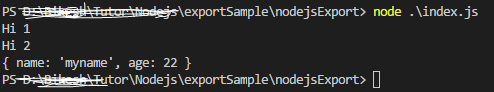
And also we can import only the specific function/data . for example I need to import only the `myMethod2()` and `myData` from the module
var m2 = require('./myutile').myMethod2; var data = require('./myutile').myData; m2(); console.log(data);
output:
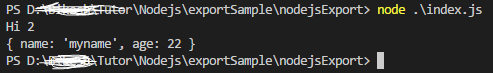
Using Typescript
sample module ‘myutile.js’
export const myMethod1 = () => { console.log('Hi 1') } export const myMethod2 = () => { console.log('Hi 2') } export const myData = { name: 'myname', age: 22 } export default { myMethod1, myMethod2, myData };
import allUtiles from './myutile'; allUtiles.myMethod1(); allUtiles.myMethod2(); console.log(allUtiles.myData);
output
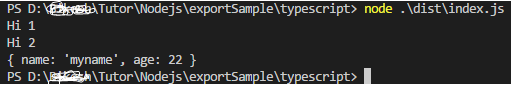
import * as allUtiles from './myutile'; allUtiles.myMethod2(); allUtiles.myMethod1(); console.log(allUtiles.myData);
output
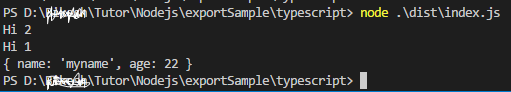
import {myMethod1,myData} from './myutile'; myMethod1(); console.log(myData);
In this sample I am using a node module called ‘ ExcelJS‘. This will stream the data to the file instead of big data in memory (if we are keeping large amount of data in memory, we may get `JavaScript heap out of memory` exception ) this will write to the file
Install the module using npm
npm install exceljs --save
then in the node application just import the module
const Excel = require('exceljs'); const options = { filename: 'myfile.xlsx', useStyles: true, useSharedStrings: true }; const workbook = new Excel.stream.xlsx.WorkbookWriter(options); const worksheet = workbook.addWorksheet('my sheet'); worksheet.columns = [ { header: 'Id', key: 'id' }, { header: 'First Name', key: 'first name' }, { header: 'Phone', key: 'ph' } ] var data; for(let i = 1; i<= 10; i++){ data = { id: i, 'first name': "name "+i, ph: "012014520"+i }; worksheet.addRow(data).commit(); } workbook.commit().then(function() { console.log('excel file cretaed'); });
we can use the same module in typescript also
refer : exceljs
Codeigniter create custom config
Create config file in ‘application\config’ folder, give any name (for example I have given ‘cust_settings.php’ [application\config\cust_settings.php] )
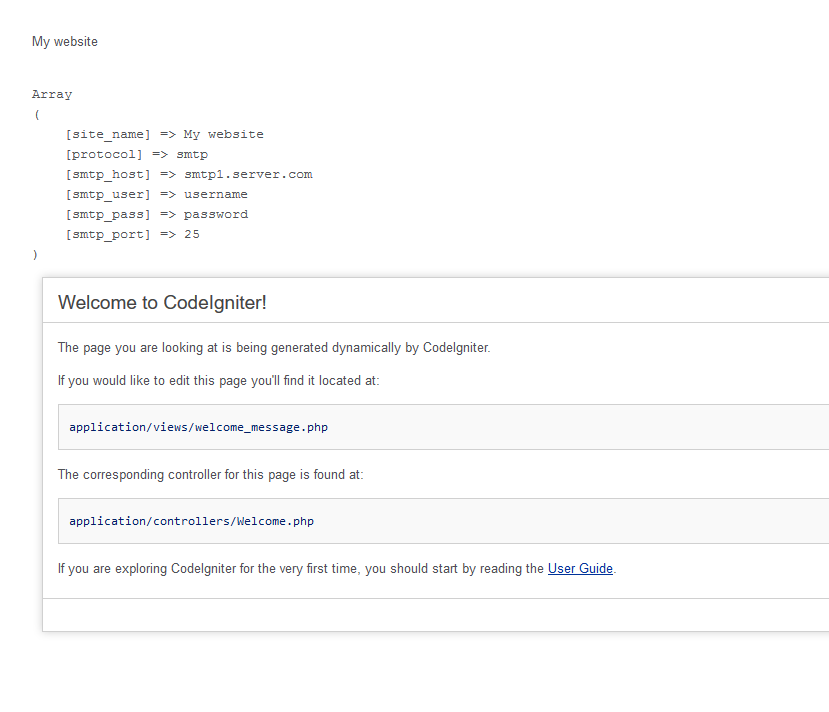
<?php if (!defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed'); $config['site_name'] = 'My website'; $config['protocol'] = 'smtp'; $config['smtp_host'] = 'smtp1.server.com'; $config['smtp_user'] = 'username'; $config['smtp_pass'] = 'password'; $config['smtp_port'] = '25';
You can use ‘config->load()’ function to load the configuration and ‘$this->config->item()’ to retrieve the configuration values
<?php defined('BASEPATH') OR exit('No direct script access allowed'); class Welcome extends CI_Controller { public function index() { // Loads a config file named cust_settings.php and assigns it to an index named "cust_settings" $this->config->load('cust_settings', TRUE); // Retrieve a config item named site_name contained within the cust_settings array $site_name = $this->config->item('site_name', 'cust_settings'); echo $site_name."<br><br>"; // An alternate way to specify the same item: $cust_settings = $this->config->item('cust_settings'); //$site_name = $cust_settings['site_name']; echo "<pre>"; print_r($cust_settings); echo "</pre>"; $this->load->view('welcome_message'); } }
Output
For using this we can load multiple configuration files
ref: codeigniter.com
In the bellow example, getting list of person id not exist in the given list
SELECT E.person_id FROM (VALUES (661), (1826), (2036), (2567), (2922), (3408) ) E(person_id) WHERE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM persontable P WHERE E.person_id = P.id )
SELECT E.email FROM (VALUES ('email1@test.com'), ('email2@test.com'), ('email3@test.com'), ('email4@test.com') ) E(email) WHERE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM person P WHERE E.email = P.emailid )
tested in PostgreSQL
Add the following code in function.php to enable or start session in wordpress
add_action('init', 'activate_session', 1); function activate_session() { if(!session_id()) { session_start(); } }
This is a basic example for beginners for creating a basic java spring boot application using ‘spring-boot-starter-parent’.
In this tutorial I am using Spring tool suite as my IDE.
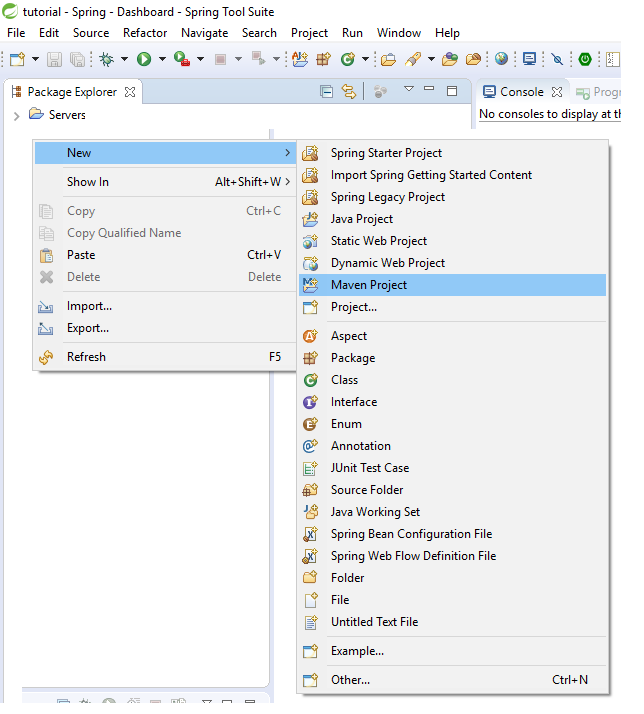
I.1: File->New -> Maven Project (You can do it by write clicking in the blank space of Package Explorer )
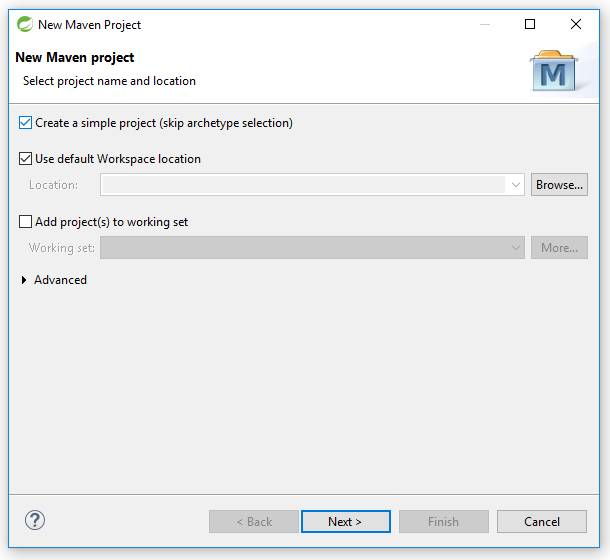
I.2: I have selected ‘create a simple project ( skip archetye selection)’ this allow me to kip the Archetype selection
I.3 : Setting group id and artifact id and other project related details
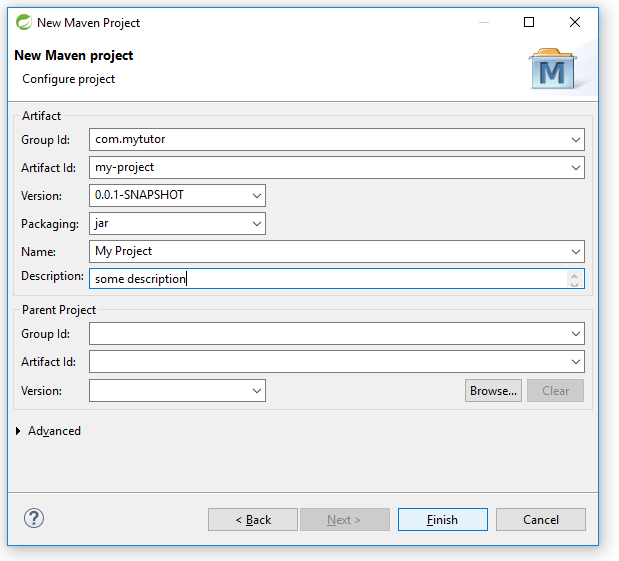
Done with the maven project creation, you can see the IDE automatically create the project folder structure like bellow .
You can see the project details in pom.xml file
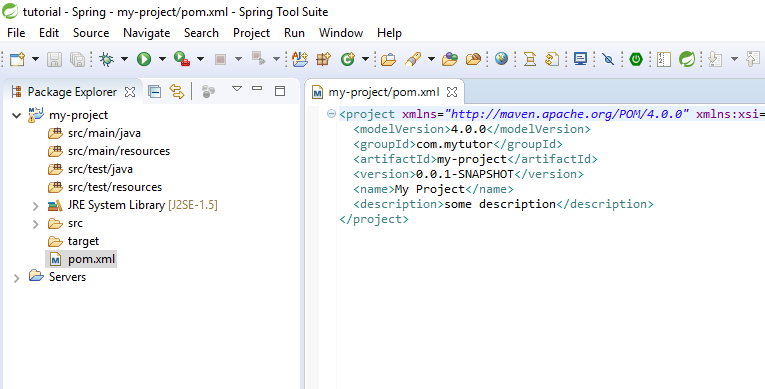
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.mytutor</groupId> <artifactId>my-project</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>My Project</name> <description>some description</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <!-- Setting java version --> </properties> <parent> <!-- here we are saying our project is a child of the spring-boot-starter-parent project --> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.3.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <!-- Adding spring boot dependency --> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
write click on project folder->Maven->Update Project
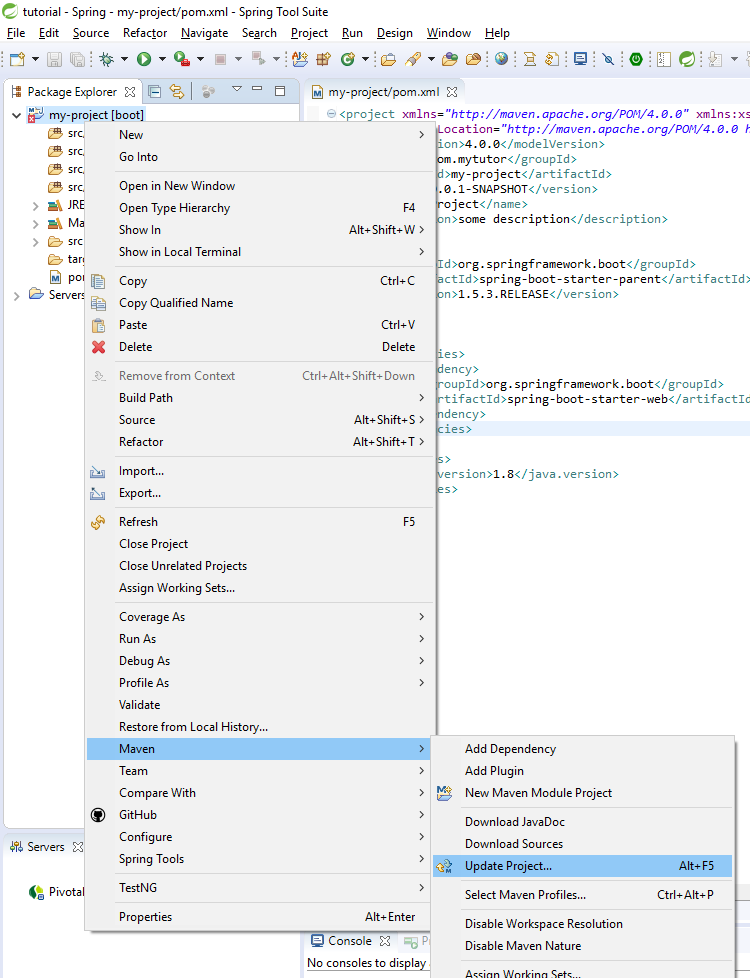
After update we can see JRe updated to 1.8 and added Maven Dependencies
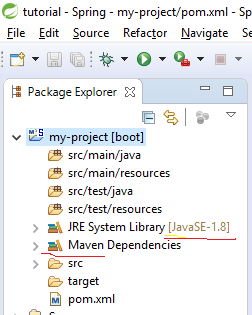
Now we can create our application entry point
Crate a class like bellow (sselect the tic ‘public static void main’ to auto generate the function)
Right click in Package Explorer -> New ->Class
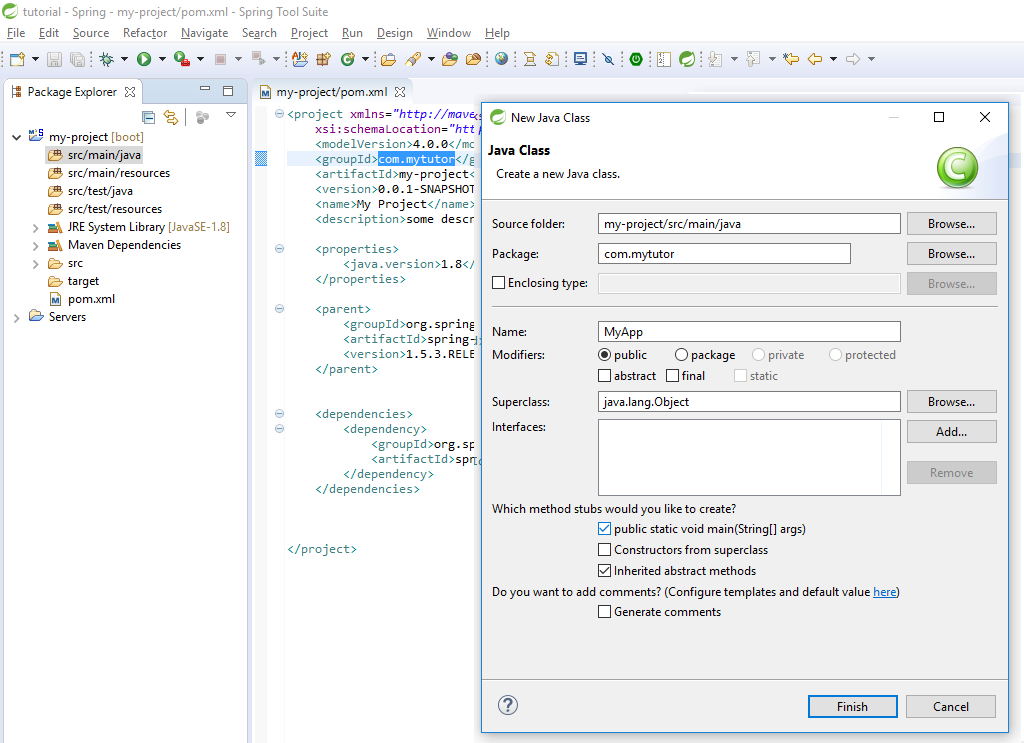
Then add @SpringBootApplication annotation to the class and add SpringApplication.run(MyApp.class, args); inside the main function
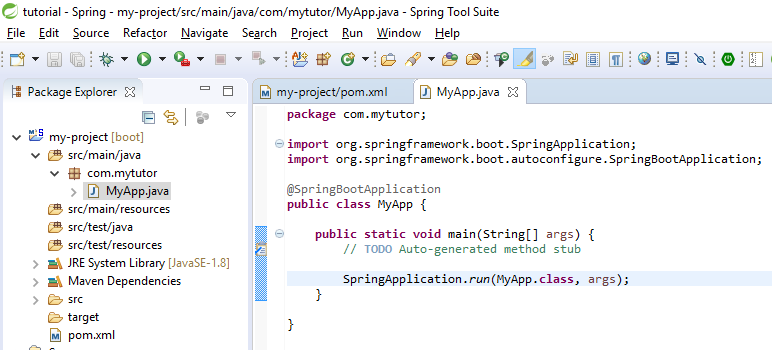
package com.mytutor; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class MyApp { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub SpringApplication.run(MyApp.class, args); } }
Now we can create our controller
Right click in Package Explorer -> New ->Class
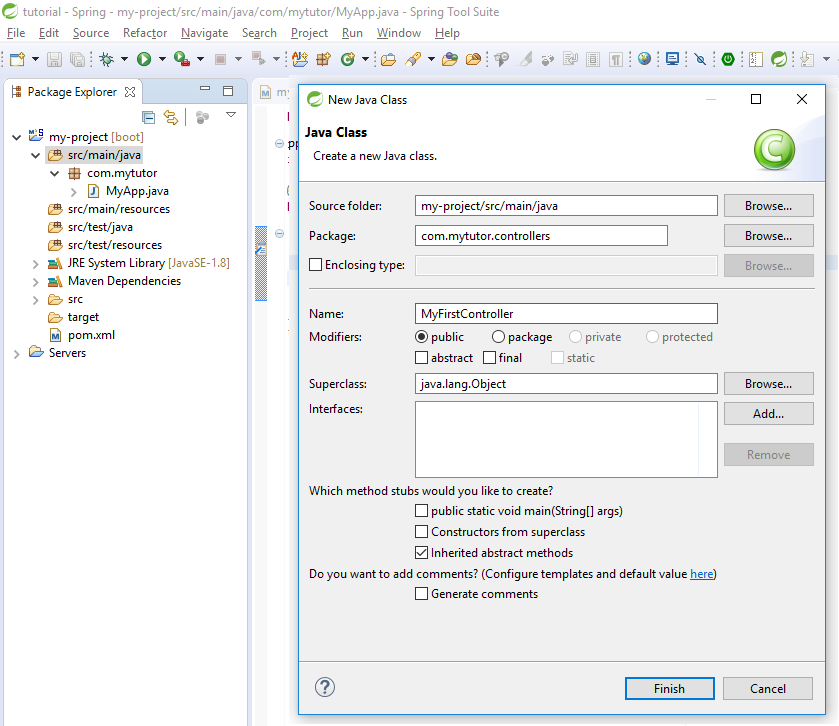
Add the following code in the file
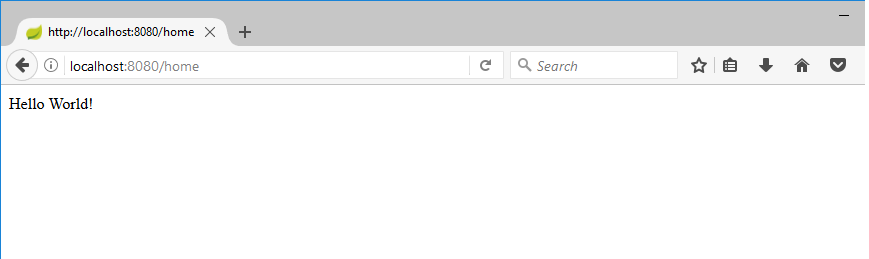
package com.mytutor.controllers; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class MyFirstController { @RequestMapping("/home") //Request mapping https://localhost/home String myHome() { return "Hello World!"; } }
You are done
Now we can run our application You can press the Green *Play button  Or you can right click the project folder and select the Run As – >Java Application
Or you can right click the project folder and select the Run As – >Java Application
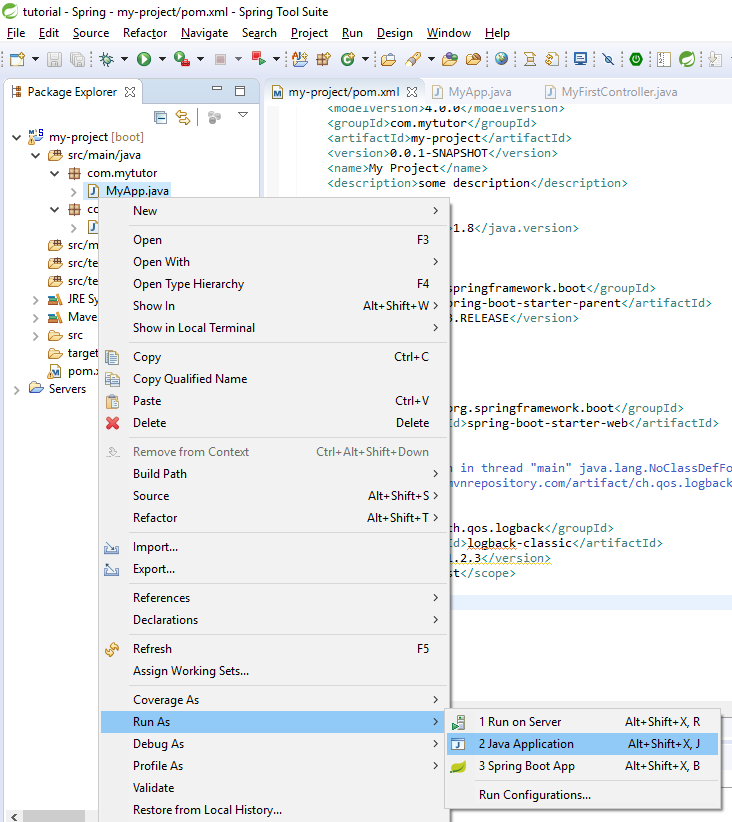
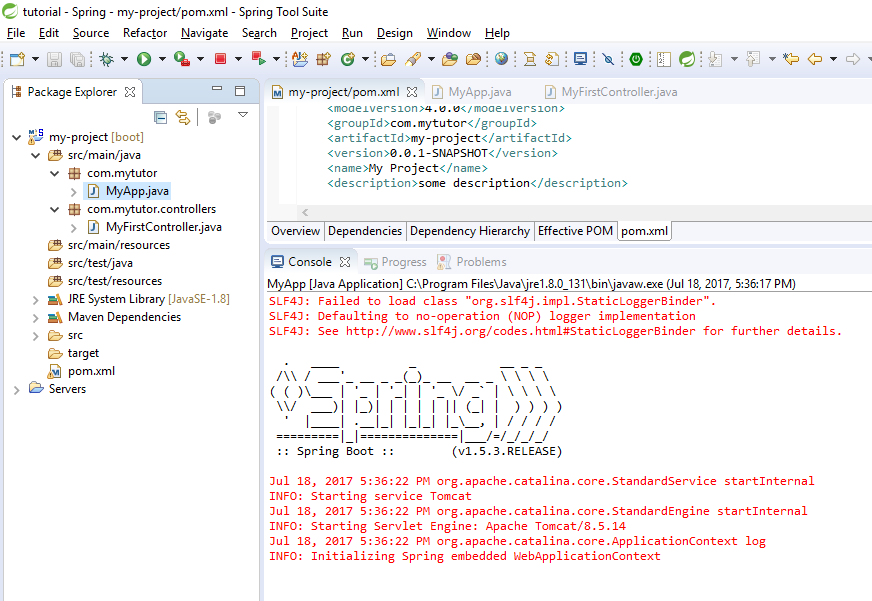
Tadaaaaa! Our project is running
Now we can hit the url
We and run Spring boot application from command line also by using the command mvn spring-boot:run
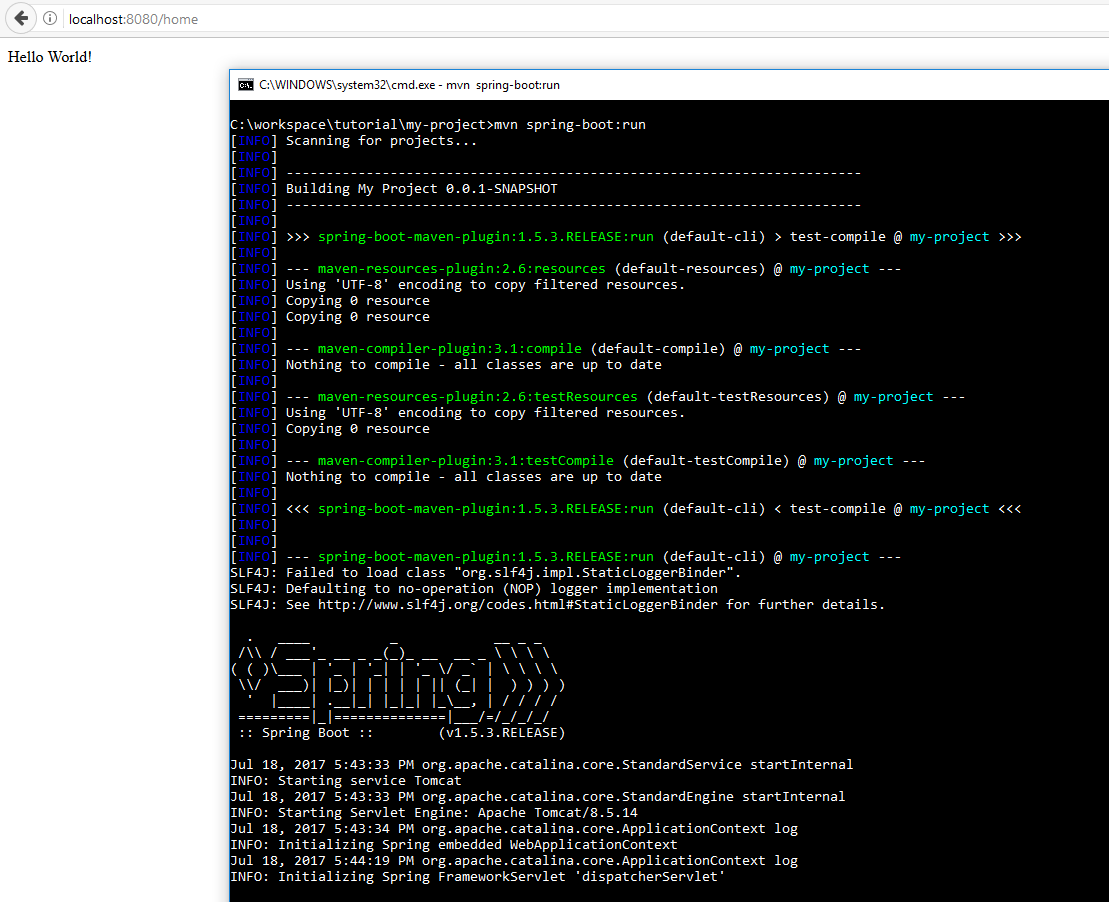
Done
Note
If you are getting the error “Exception in thread “main” java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: ch/qos/logback/classic/turbo/TurboFilter ” please add the logback-classic dependency in pom file
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: ch/qos/logback/classic/turbo/TurboFilter --> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/ch.qos.logback/logback-classic --> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <version>1.2.3</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>